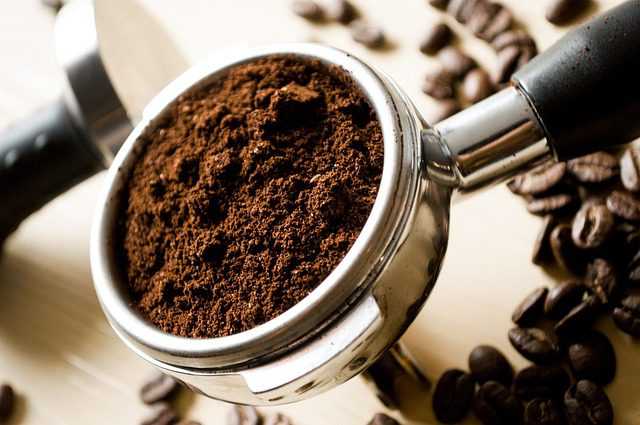
OVIEDO, Fla., USA – Coffee has helped power people for years. Now, coffee and other bio-based resources may help power lithium-ion batteries, thanks to breakthrough technology from X-BATT. X-BATT, a pioneer in advanced material solutions, today announced a significant breakthrough in lithium-ion battery technology with the introduction of its innovative composite anode materials utilizing renewable, bio-derived materials.
This cutting-edge research sets a new standard for sustainable and efficient energy storage applications.
X-BATT’s research targets the pressing need for alternative anode materials in the face of skyrocketing demand for lithium-ion batteries.
By leveraging agricultural waste products as a low-cost carbon source, X-BATT aims to address the critical mineral shortage threatening the electrification movement by replacing or supplementing graphite with abundant, renewable resources while promoting carbon sequestration, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and fostering sustainable economic growth.
X-BATT’s approach involves the use of Polymer Derived Ceramic (PDC) composite materials.
Through patented materials synthesis processes, the company has demonstrated the ability to incorporate various biobased carbon sources into high-energy dense anode materials.
This technology has shown promising results in initial screenings and offers a viable pathway to create sustainable, high-performance lithium-ion batteries.
The research underscores the potential of biobased resources such as wood, bamboo, corn husk, rice husk, and even spent coffee grounds in producing anode materials that exhibit higher reversible specific capacity and better rate capability than traditional graphite in batteries.
This not only reduces dependence on foreign sources for critical materials but also leverages agricultural waste, presenting a circular economy model for utilizing low-value waste materials in high-value applications.
“Our proposed technology represents a leap forward in the quest for sustainable energy solutions,” said Bill Easter, CEO of X-BATT. “By harnessing the power of bio-derived materials, we’re not just innovating for the sake of progress; we’re addressing global challenges of resource scarcity, environmental impact, and energy security. Our work paves the way for a future where batteries are not only more efficient but also more aligned with the principles of sustainability and renewable energy.”
As X-BATT moves into the next phases of research and development, the company is committed to collaborating with government national labs, private and public companies, and universities. The goal is to further develop, test, and eventually commercialize this groundbreaking technology, with the potential to significantly impact the global energy storage market.