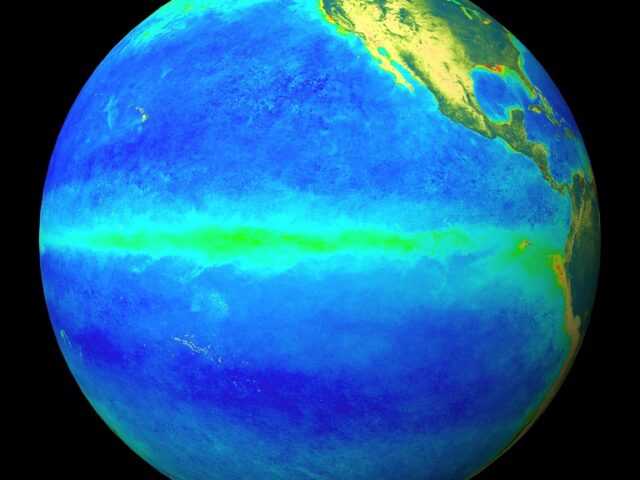
MELBOURNE, Australia – The Australian Bureau of Meteorology’s ENSO Outlook has been raised to La Niña ALERT. This is due to continued cooling in the tropical Pacific Ocean and an increase in the number of climate models showing sustained La Niña conditions over summer. Historically, when La Niña ALERT criteria have been met, La Niña has subsequently developed around 70% of the time.
A 70% chance of an event is approximately triple the normal likelihood. La Niña events increase the chances of above-average rainfall for northern and eastern Australia during spring and summer.
Most oceanic and atmospheric indicators of ENSO are currently within the ENSO-neutral range, but some have shifted towards a La Niña-like state. Sea surface temperatures in the central tropical Pacific Ocean are neutral, but have cooled over the past three months and are supported by cooler than average waters beneath the surface.
Some atmospheric indicators, such as the Southern Oscillation Index (SOI) and cloudiness near the Date Line, are approaching La Niña levels. Six of the seven international climate models surveyed by the Bureau meet La Niña criteria from November.
A weak negative Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) event continues. Most models suggest the negative IOD event will ease to neutral levels in late spring. A negative IOD increases the chances of above-average spring rainfall for much of southern and eastern Australia, while a neutral IOD has little influence on Australian climate.
The Madden–Julian Oscillation (MJO) has been active over the Maritime Continent since late September. The MJO is forecast to progress eastwards over the coming week and weaken as it approaches the western Pacific. While the MJO is over the Maritime Continent region, it encourages enhanced rainfall over the tropics to the north of Australia.
The Southern Annular Mode (SAM) index has been neutral for the past week after 5 to 6 weeks at positive levels. While it is forecast to remain neutral for the coming week, it is expected to return to generally positive levels from October to December. A positive SAM during spring typically brings wetter weather to eastern parts of Australia, but drier than average conditions for western Tasmania.
Climate change continues to influence Australian and global climate. Australia’s climate has warmed by around 1.44 °C for the 1910–2019 period. Rainfall across northern Australia during its wet season (October–April) has increased since the late 1990s. In recent decades there has been a trend towards a greater proportion of rainfall from high intensity short duration rainfall events, especially across northern Australia.